Difference between revisions of "Tutorial/Heat equation with Dirichlet boundary control"
(→The considered problem) |
m (Geuzaine moved page Heat equation with Dirichlet boundary control to Tutorial/Heat equation with Dirichlet boundary control) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
$$ | $$ | ||
| − | Physically, these problems model the diffusion of the temperature | + | Physically, these problems model the diffusion of the temperature on the annulus over time. The Dirichlet boundary condition models the fact that the temperature on the boundary $\Gamma_0$ is maintained to $0$ (for instance, we put the system in a bowl of ice), as the Neumann boundary condition models the fact that the temperature on the boundary $\Gamma_0$ is let free. Furthermore, the control $u$ corresponds for instance to a thermal resistance, heating the boundary $\Gamma_1$ from $0$ to $50$ degrees. |
To solve problems \eqref{eq:problemNeu} and \eqref{eq:problemDir} using the finite element method in the space variable, we write their weak formulations: | To solve problems \eqref{eq:problemNeu} and \eqref{eq:problemDir} using the finite element method in the space variable, we write their weak formulations: | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
\begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationNeu} | \begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationNeu} | ||
\left\{\begin{array}{l} | \left\{\begin{array}{l} | ||
| − | \text{ | + | \text{Find } v_N\in C^1([0,\infty),\mathcal H_N) \text{ such that, }\\ |
| − | \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal | + | \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal H_N, t\geq 0, \qquad \int_{\Omega}\dfrac{d v_N}{dt} \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \nabla v_N\cdot\nabla \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega = 0}, |
\end{array}\right. | \end{array}\right. | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
\begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationDir} | \begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationDir} | ||
\left\{\begin{array}{l} | \left\{\begin{array}{l} | ||
| − | \text{ | + | \text{Find } v_D\in C^1([0,\infty), \mathcal H_D) \text{ such that, }\\ |
| − | \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal | + | \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal H_D, t\geq0, \qquad \int_{\Omega}\dfrac{d v_D}{dt} \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \nabla v_D\cdot\nabla \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega = 0}, |
\end{array}\right. | \end{array}\right. | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
| − | where the functions $\varphi$ are the ''test functions''. | + | where $\mathcal H_N = \{w \in H^1(\Omega) \mid w = u \text{ on } \Gamma_1 \}$, $\mathcal H_D = \{w \in H^1(\Omega) \mid w = 0 \text{ on } \Gamma_0, \; w = u \text{ on } \Gamma_1 \}$ and the functions $\varphi$ are the ''test functions''. |
| − | To solve these equations, we use the '''DtDof''' keyword of GetDP in the ''Formulation'' group to specify the derivative in the weak formulation, as in the ''Resolution'' group, we use the '''TimeLoopTheta''' keyword to indicate that we need a finite difference time scheme. | + | To solve these equations, we use the '''DtDof''' keyword of GetDP in the ''Formulation'' group to specify the derivative in time in the weak formulation, as in the ''Resolution'' group, we use the '''TimeLoopTheta''' keyword to indicate that we need a finite difference time $\theta$-scheme. |
== Outline of the program == | == Outline of the program == | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
Simply open the two .pos files with GMSH, and compare them to see the influence of the control on $\Gamma_1$ and the Neumann and Boundary conditions on $\Gamma_0$. | Simply open the two .pos files with GMSH, and compare them to see the influence of the control on $\Gamma_1$ and the Neumann and Boundary conditions on $\Gamma_0$. | ||
| − | == | + | == Results == |
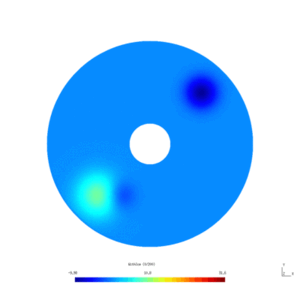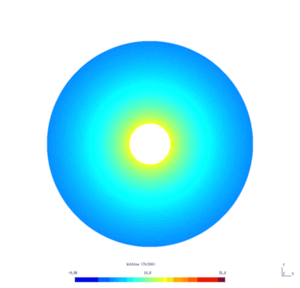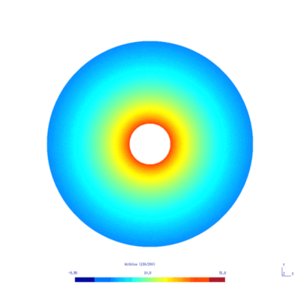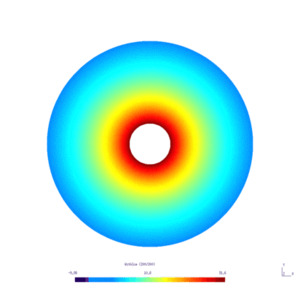
| − | Here is the | + | Here is the results obtained with GMSH/GetDP. The first and second pictures show respectively the solution $v_N$ and $v_D$, every ten steps. |
[[File:HeatWithoutIceLight.gif|300px|frameless|alt=Solution v_N.|v_N.]] | [[File:HeatWithoutIceLight.gif|300px|frameless|alt=Solution v_N.|v_N.]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 19 April 2015
Contents
The considered problem
In this problem, we consider a Heat equation with a Dirichlet control on a part of the boundary, and homogeneous Dirichlet or Neumann condition on the other part. To model this in GetDP, we will introduce a "Constraint" with "TimeFunction". We assume that the reader has already studied this previous example and this one.
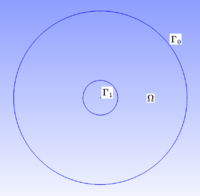
We considered the annulus $\Omega = \mathcal D (0, 1) \setminus \mathcal D (0, 0.2)$ and we seek the functions $v_N$ and $v_D$, respective solutions of the following problems
\begin{equation} \begin{cases}\label{eq:problemNeu} \dfrac{\partial}{\partial t} v_N(x,t) -\Delta v_N(x,t) = 0 & \forall x \in \Omega, t\geq0\\ \dfrac{\partial v_N}{\partial \mathbf{n}}(x,t) = 0 & \forall x \in \Gamma_0, t \geq0\\ v_N(x,t) = u(x,t) & \forall x \in \Gamma_1, t \geq0. \end{cases} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \begin{cases}\label{eq:problemDir} \dfrac{\partial}{\partial t} v_D(x,t) -\Delta v_D(x,t) = 0 & \forall x \in \Omega, t\geq0\\ v_D(x,t) = 0 & \forall x \in \Gamma_0, t \geq0\\ v_D(x,t) = u(x,t) & \forall x \in \Gamma_1, t \geq0. \end{cases} \end{equation}
where $\Gamma_0 = \partial \mathcal D (0, 1)$ is the boundary of $\mathcal D (0, 1)$, $\Gamma_1 = \partial \mathcal D (0, 0.2)$ is the boundary of $\mathcal D (0, 0.2)$ and $\displaystyle{\Delta = \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x_1^2} + \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x_2^2} }$ is the Laplace operator.
To simplify, we suppose that the control $u$ is defined by $$ \forall (x,y)\in \Gamma_1, t\geq0 \qquad u(x,y,t) = u(t) = 50(1-\exp(-0.5t)). $$
Physically, these problems model the diffusion of the temperature on the annulus over time. The Dirichlet boundary condition models the fact that the temperature on the boundary $\Gamma_0$ is maintained to $0$ (for instance, we put the system in a bowl of ice), as the Neumann boundary condition models the fact that the temperature on the boundary $\Gamma_0$ is let free. Furthermore, the control $u$ corresponds for instance to a thermal resistance, heating the boundary $\Gamma_1$ from $0$ to $50$ degrees.
To solve problems \eqref{eq:problemNeu} and \eqref{eq:problemDir} using the finite element method in the space variable, we write their weak formulations:
\begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationNeu} \left\{\begin{array}{l} \text{Find } v_N\in C^1([0,\infty),\mathcal H_N) \text{ such that, }\\ \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal H_N, t\geq 0, \qquad \int_{\Omega}\dfrac{d v_N}{dt} \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \nabla v_N\cdot\nabla \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega = 0}, \end{array}\right. \end{equation}
\begin{equation}\label{eq:WeakFormulationDir} \left\{\begin{array}{l} \text{Find } v_D\in C^1([0,\infty), \mathcal H_D) \text{ such that, }\\ \displaystyle{\forall \varphi\in \mathcal H_D, t\geq0, \qquad \int_{\Omega}\dfrac{d v_D}{dt} \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega + \int_{\Omega} \nabla v_D\cdot\nabla \varphi \;{\rm d}\Omega = 0}, \end{array}\right. \end{equation} where $\mathcal H_N = \{w \in H^1(\Omega) \mid w = u \text{ on } \Gamma_1 \}$, $\mathcal H_D = \{w \in H^1(\Omega) \mid w = 0 \text{ on } \Gamma_0, \; w = u \text{ on } \Gamma_1 \}$ and the functions $\varphi$ are the test functions.
To solve these equations, we use the DtDof keyword of GetDP in the Formulation group to specify the derivative in time in the weak formulation, as in the Resolution group, we use the TimeLoopTheta keyword to indicate that we need a finite difference time $\theta$-scheme.
Outline of the program
The proposed solution is composed by 2 different files:
- Annulus.geo
- GMSH file, used to build both the square $\Omega$ and its boundary $\Gamma_0$ and $\Gamma_1$.
- Heat.pro
- GetDP file, contains the weak formulations \eqref{eq:WeakFormulationNeu} and \eqref{eq:WeakFormulationDir} of the problems \eqref{eq:problemNeu} and \eqref{eq:problemDir}.
Annulus.geo: creation of the geometry with GMSH
/* -----------------------
File Annulus.geo
----------------------- */
// Mesh step h :
h = 0.025;
/*==============*/
/* Large Circle */
/*==============*/
// Points :
Point(1) = {0,0,0,h};
Point(2) = {1,0,0,h};
Point(3) = {0,1,0,h};
Point(5) = {-1,0,0,h};
Point(6) = {0,-1,0,h};
// Arcs :
Circle(1) = {2,1,3};
Circle(2) = {3,1,5};
Circle(3) = {5,1,6};
Circle(4) = {6,1,2};
// Circle :
Line Loop(1) = {1,2,3,4};
/*===============*/
/* Little Circle */
/*===============*/
// Points :
Point(200) = {0.2,0,0,h};
Point(300) = {0,0.2,0,h};
Point(500) = {-0.2,0,0,h};
Point(600) = {0,-0.2,0,h};
// Arcs :
Circle(100) = {200,1,300};
Circle(200) = {300,1,500};
Circle(300) = {500,1,600};
Circle(400) = {600,1,200};
// Circle :
Line Loop(100) = {100,200,300,400};
/*=======*/
/* Omega */
/*=======*/
// Annulus : The surface between the little circle and the large circle
Plane Surface(1) = {1, 100};
/*===================*/
/* Physical Entities */
/*===================*/
// Gama0
Physical Line(1001) = {1,2,3,4};
// Gama1
Physical Line(1002) = {100,200,300,400};
// Omega
Physical Surface(1005) = {1};
Direct link to file `Heat/GMSH_GETDP/Annulus.geo'
Heat.pro: weak formulations
/* -----------------------
File Heat.pro
----------------------- */
/*======================
Geometrical Entities
======================*/
Group {
// Boundary
Gama0 = Region[ 1001 ];
Gama1 = Region[ 1002 ];
// The Domain
Omega = Region[ 1005 ];
// The Boundary And The Domain
AllOmega = Region[{Omega,Gama0,Gama1}];
}
/*=====================
Some Functions
=====================*/
Function {
// Initial State
InitialState[AllOmega] = 10*Exp[-25*((X[]+0.5)*(X[]+0.5)+(Y[]+0.5)*(Y[]+0.5))] - 5*Exp[-50*((X[]+0.3)*(X[]+0.3)+(Y[]+0.5)*(Y[]+0.5))] - 10*Exp[-45*((X[]-0.5)*(X[]-0.5)+(Y[]-0.5)*(Y[]-0.5))];
// Control (= Heating on Gama1)
u[] = 50*(1-Exp[-0.5*$Time]);
// Time Discretization
t0 = 0.;
T = 2.;
dt = 0.01;
// Type of Scheme (See Crank-Nicolson on the manual)
gamma = 0.5;
}
/*===============================
Constraints and Initial State
===============================*/
Constraint {
// Initial State
{ Name InitialData; Type Init;
Case {
{ Region Omega; Value InitialState[]; }
}
}
// Boundary control
{ Name Resistance; Type Assign;
Case {
{ Region Gama1; Value 1.; TimeFunction u[]; }
}
}
// Boundary Dirichlet Condition (Ice on Gama0)
{ Name Ice; Type Assign;
Case {
{ Region Gama0; Value 0.; }
}
}
}
/*====================
Functional Spaces
====================*/
FunctionSpace {
{ Name VhNeu; Type Form0;
BasisFunction{
{ Name wn; NameOfCoef vn; Function BF_Node;
Support AllOmega; Entity NodesOf[All];}
}
Constraint {
{ NameOfCoef vn; EntityType NodesOf;
NameOfConstraint Resistance; }
{ NameOfCoef vn; EntityType NodesOf;
NameOfConstraint InitialData; }
}
}
{ Name VhDir; Type Form0;
BasisFunction{
{ Name wn; NameOfCoef vn; Function BF_Node;
Support AllOmega; Entity NodesOf[All];}
}
Constraint {
{ NameOfCoef vn; EntityType NodesOf;
NameOfConstraint Resistance; }
{ NameOfCoef vn; EntityType NodesOf;
NameOfConstraint Ice; }
{ NameOfCoef vn; EntityType NodesOf;
NameOfConstraint InitialData; }
}
}
}
/*====================
Jacobian
====================*/
Jacobian {
{ Name JVol ;
Case {
{ Region All ; Jacobian Vol ; }
}
}
{ Name JSur ;
Case {
{ Region All ; Jacobian Sur ; }
}
}
{ Name JLin ;
Case {
{ Region All ; Jacobian Lin ; }
}
}
}
/*======================
Integral Parameters
======================*/
Integration {
{ Name I1 ;
Case {
{ Type Gauss ;
Case {
{ GeoElement Point ; NumberOfPoints 1 ; }
{ GeoElement Line ; NumberOfPoints 4 ; }
{ GeoElement Triangle ; NumberOfPoints 6 ; }
{ GeoElement Quadrangle ; NumberOfPoints 7 ; }
{ GeoElement Tetrahedron ; NumberOfPoints 15 ; }
{ GeoElement Hexahedron ; NumberOfPoints 34 ; }
}
}
}
}
}
/*======================
Weak formulations
======================*/
Formulation {
{ Name Heat; Type FemEquation;
Quantity{
{ Name w; Type Local; NameOfSpace VhNeu;}
{ Name v; Type Local; NameOfSpace VhDir;}
}
Equation{
// Without Ice, i.e. Neumann boundary condition on Gama0
Galerkin{ DtDof [ Dof{w}, {w} ];
In Omega; Jacobian JVol; Integration I1;}
Galerkin{ [ Dof{Grad w}, {Grad w} ];
In Omega; Jacobian JVol; Integration I1;}
// With Ice, i.e. Dirichlet boundary condition on Gama0
Galerkin{ DtDof [ Dof{v}, {v} ];
In Omega; Jacobian JVol; Integration I1;}
Galerkin{ [ Dof{Grad v}, {Grad v} ];
In Omega; Jacobian JVol; Integration I1;}
}
}
}
/*======================
Resolution
======================*/
Resolution {
{ Name HeatSolver;
System{
{ Name SysHeat; NameOfFormulation Heat;}
}
Operation{
// Initialisation
InitSolution[SysHeat];
// Computation on [t0,T]
TimeLoopTheta[t0, T, dt, gamma ] {
Generate[SysHeat]; Solve[SysHeat];
}
}
}
}
/*==============
Post Processing
==============*/
PostProcessing {
{ Name HeatSolver; NameOfFormulation Heat; NameOfSystem SysHeat;
Quantity{
{ Name WithoutIce; Value {Local{[{w}]; In AllOmega; Jacobian JVol;}}}
{ Name WithIce; Value {Local{[{v}]; In AllOmega; Jacobian JVol;}}}
}
}
}
/*=============
Post Operation
=============*/
PostOperation {
{Name Map_Omega; NameOfPostProcessing HeatSolver;
Operation{
Print[WithoutIce, OnElementsOf AllOmega, File "HeatOnOmegaWithoutIce.pos"];
Print[WithIce, OnElementsOf AllOmega, File "HeatOnOmegaWithIce.pos"];
}
}
}
Direct link to file `Heat/GMSH_GETDP/Heat.pro'
How to launch
The procedure is the same as described in this example, but we recall it here. Let us recall that all files (.geo and .pro) must be located in the same directory. We just describe the procedure using a terminal.
- Meshing the domain
In the right directory, type:
- gmsh Annulus.geo -algo iso -2
After that, a file Annulus.msh should have been created.
- Solving the problem
Type the following command in the terminal:
- getdp Heat.pro -solve '#1' -pos '#1' -mesh Annulus.msh
- Displaying the result
Simply open the two .pos files with GMSH, and compare them to see the influence of the control on $\Gamma_1$ and the Neumann and Boundary conditions on $\Gamma_0$.
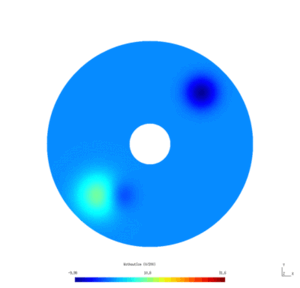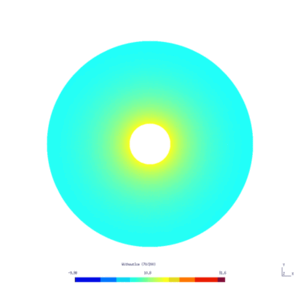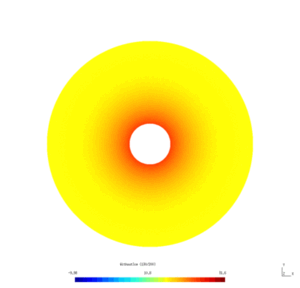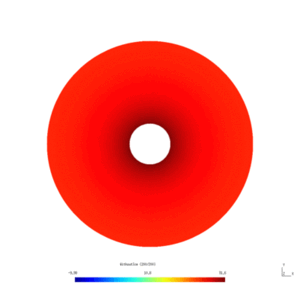
Results
Here is the results obtained with GMSH/GetDP. The first and second pictures show respectively the solution $v_N$ and $v_D$, every ten steps.
All files
A zipfile containing all files (.geo, .pro, .mesh and .gif with all Time Steps, the .pos are too big) can be downloaded here.