Difference between revisions of "Electromechanical relay"
From ONELAB
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{metamodelGetDP|relay}} |
== Additional information == | == Additional information == | ||
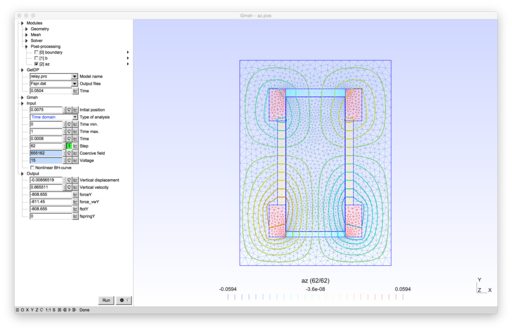
| − | + | This is a 2D model of a linear actuator <ref name=Sab2003 /><ref name=Sab2004_phd />. It comprises a yoke, two permanent magnets, two coils and a mover. The yoke and the mover are made of iron. Eddy currents in the magnets and in the laminated yoke and mover are neglected. The permanent magnets constitute a magnetic lock that keeps the mover either in the upper or lower position tending to diminish the residual airgap. The mover is moved down or up by applying a voltage pulse to one of the coils. The commutation is facilitated by two springs. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | To run the example, simply open '''relay.pro''' in Gmsh. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| − | <ref name=Sab2003>R. V. Sabariego, J. Gyselinck, C. Geuzaine, P. Dular, W. Legros, [http://orbi.ulg.ac.be/handle/2268/22765 | + | <ref name=Sab2003>R. V. Sabariego, J. Gyselinck, C. Geuzaine, P. Dular, W. Legros, [http://orbi.ulg.ac.be/handle/2268/22765 Application of the fast multipole method to the 2D finite element-boundary element analysis of electromechanical devices], COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation |
and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 22(3):659-673, 2003.</ref> | and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 22(3):659-673, 2003.</ref> | ||
| − | <ref name=Sab2004_phd> R. V. Sabariego, [http://hdl.handle.net/2268/2374 | + | <ref name=Sab2004_phd> R. V. Sabariego, [http://hdl.handle.net/2268/2374 The fast multipole method for electromagnetic field computation in numerical and physical hybrid systems], Ph.D. thesis, University of Liège, 2004.</ref> |
</references> | </references> | ||
<div class="references-small"> <references /> </div> | <div class="references-small"> <references /> </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{metamodelfooter|relay}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:58, 25 July 2015
|
2D model of an electro-mechanical relay.
|
|
|---|
|
Download model archive (relay.zip) |
Additional information
This is a 2D model of a linear actuator [1][2]. It comprises a yoke, two permanent magnets, two coils and a mover. The yoke and the mover are made of iron. Eddy currents in the magnets and in the laminated yoke and mover are neglected. The permanent magnets constitute a magnetic lock that keeps the mover either in the upper or lower position tending to diminish the residual airgap. The mover is moved down or up by applying a voltage pulse to one of the coils. The commutation is facilitated by two springs.
To run the example, simply open relay.pro in Gmsh.
References
- ↑ R. V. Sabariego, J. Gyselinck, C. Geuzaine, P. Dular, W. Legros, Application of the fast multipole method to the 2D finite element-boundary element analysis of electromechanical devices, COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 22(3):659-673, 2003.
- ↑ R. V. Sabariego, The fast multipole method for electromagnetic field computation in numerical and physical hybrid systems, Ph.D. thesis, University of Liège, 2004.
|
Model developed by R. Sabariego.
|

