Difference between revisions of "Electric machines"
From ONELAB
(→Additional information) |
(→Additional information) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* '''im.pro''': a four-pole induction machine <ref>S. Guérard, J. Gyselinck, and J. Lecomte-Beckers,[http://hdl.handle.net/2268/38463 "Finite element modelling of an asynchronous motor with one broken rotor bar, comparison with the data recorded on a prototype and material aspects"], Bulletin Scientifique de l'AIM, Vol.1, pp. 13-22, 2005. | * '''im.pro''': a four-pole induction machine <ref>S. Guérard, J. Gyselinck, and J. Lecomte-Beckers,[http://hdl.handle.net/2268/38463 "Finite element modelling of an asynchronous motor with one broken rotor bar, comparison with the data recorded on a prototype and material aspects"], Bulletin Scientifique de l'AIM, Vol.1, pp. 13-22, 2005. | ||
Prix Melchior Salier 2004 du meilleur travail de fin d'études section électromécanique-énergétique.</ref> | Prix Melchior Salier 2004 du meilleur travail de fin d'études section électromécanique-énergétique.</ref> | ||
| − | * '''t30.pro''': induction motor with solid rotor <ref> [http://www.compumag.org/jsite/team.html International TEAM Workshop Problem 30a | + | * '''t30.pro''': induction motor with solid rotor <ref> [http://www.compumag.org/jsite/team.html International TEAM Workshop Problem 30a - Induction Motor Analyses], Kent Davey</ref> |
== References == | == References == | ||
<div class="references-small"> <references /> </div> | <div class="references-small"> <references /> </div> | ||
Revision as of 07:25, 16 May 2013
|
2D models of electric machines: permanent magnet and wound field synchronous machines, induction machines, switched reluctance machine.
|
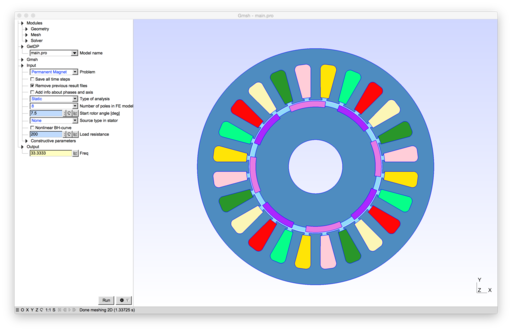 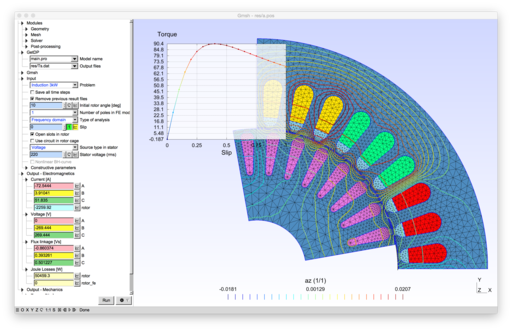
|
|---|
|
Download model archive (machines.zip) |
Additional information
The example contains:
- pmsm.pro: an eight-pole permanent magnet synchronous machine from GRUCAD, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Brazil [1]
- pmsm_cbmag.pro: variant of eight-pole permanent magnet synchronous machine from GRUCAD, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Brazil (actual geometry with no simplifications) [2][3]
- lomonova.pro: an eight-pole permanent magnet machine [4]
- wfsm_4p.pro: a four-pole wound field synchronous machine [5]
- im.pro: a four-pole induction machine [6]
- t30.pro: induction motor with solid rotor [7]
References
- ↑ M. V. Ferreira da Luz, P. Dular, N. Sadowski, C. Geuzaine, and J. P. A. Bastos, "Analysis of a Permanent Magnet Generator With Dual Formulations Using Periodicity Conditions and Moving Band", IEEE Trans. Mag., Vol 38, No. 2, pp. 961-964, 2002.
- ↑ J. Gyselinck, N. Sadowski, P. Dular, M. V. Ferreira da Luz, J. P. A. Bastos, and W. Legros, "Harmonic Balance Finite Element Modelling of a Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine", Proceedings of CBMag 2002.
- ↑ J. Gyselinck, P. Dular, L. Vandevelde and J. Melkebeek, A.M. Oliveira and P. Kuo-Peng,"Two-dimensional harmonic balance finite element modelling of electrical machines taking motion into account", COMPEL, Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 1021-1036, 2003.
- ↑ E.A. Lomonova, E. Kazmin, Y. Tang, J.J.H. Paulides, "In-wheel PM Motor: Compromise between High Power Density and Extended Speed Capability", COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 98-116, 2011.
- ↑ J. Gyselinck, L. Vandevelde, J. Melkebeek, W. Legros, "Steady-State Finite Element Analysis of a Salient-Pole Synchronous Machine in the Frequency Domain", Proceedings Electrimacs 2002, Montréal, Canada, August 18-21, 6 p.
- ↑ S. Guérard, J. Gyselinck, and J. Lecomte-Beckers,"Finite element modelling of an asynchronous motor with one broken rotor bar, comparison with the data recorded on a prototype and material aspects", Bulletin Scientifique de l'AIM, Vol.1, pp. 13-22, 2005. Prix Melchior Salier 2004 du meilleur travail de fin d'études section électromécanique-énergétique.
- ↑ International TEAM Workshop Problem 30a - Induction Motor Analyses, Kent Davey

