Difference between revisions of "Electric machines"
From ONELAB
(→References) |
(→Additional information) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
* '''im.pro''': a four-pole deep-bar induction machine <ref>S. Guérard, J. Gyselinck, and J. Lecomte-Beckers,[http://hdl.handle.net/2268/38463 "Finite element modelling of an asynchronous motor with one broken rotor bar, comparison with the data recorded on a prototype and material aspects"], Bulletin Scientifique de l'AIM, Vol.1, pp. 13-22, 2005. | * '''im.pro''': a four-pole deep-bar induction machine <ref>S. Guérard, J. Gyselinck, and J. Lecomte-Beckers,[http://hdl.handle.net/2268/38463 "Finite element modelling of an asynchronous motor with one broken rotor bar, comparison with the data recorded on a prototype and material aspects"], Bulletin Scientifique de l'AIM, Vol.1, pp. 13-22, 2005. | ||
Prix Melchior Salier 2004 du meilleur travail de fin d'études section électromécanique-énergétique.</ref> | Prix Melchior Salier 2004 du meilleur travail de fin d'études section électromécanique-énergétique.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{reflist|refs= | ||
| + | <ref name=Ferreira2002>M. V. Ferreira da Luz, P. Dular, N. Sadowski, C. Geuzaine, and J. P. A. Bastos, [http://orbi.ulg.ac.be/handle/2268/22771 "Analysis of a permanent magnet generator with dual formulations using periodicity conditions and moving band"], IEEE Trans. Mag., Vol 38, No. 2, pp. 961-964, 2002.</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=Gyselinck2002>J. Gyselinck, N. Sadowski, P. Dular, M. V. Ferreira da Luz, J. P. A. Bastos, and W. Legros, [http://hdl.handle.net/2013/ULB-DIPOT:oai:dipot.ulb.ac.be:2013/73090 "Harmonic balance finite element modelling of a permanent-magnet synchronous machine"], Proceedings of CBMag 2002.</ref> | ||
| + | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<div class="references-small"><references \> </div> | <div class="references-small"><references \> </div> | ||
{{metamodelfooter|machines}} | {{metamodelfooter|machines}} | ||
Revision as of 09:37, 18 July 2013
|
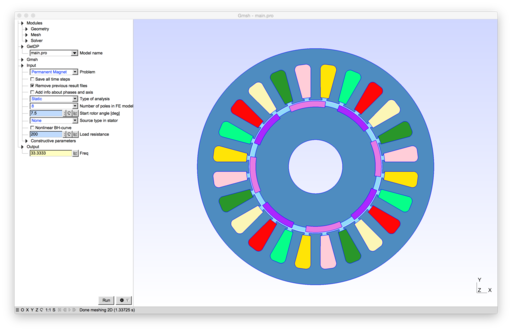
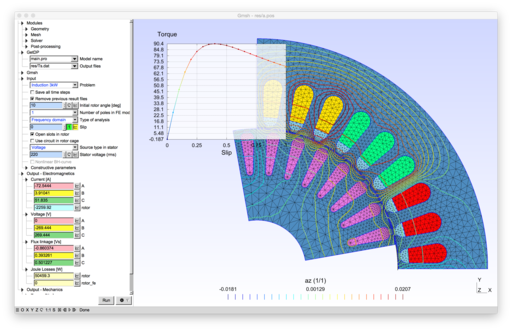
2D models of electric machines: permanent magnet and wound field synchronous machines, induction machines, switched reluctance machine.
|
|
|---|
|
Download model archive (machines.zip) |
Additional information
The example contains:
- pmsm.pro and pmsm_cbmag.pro: an eight-pole permanent magnet synchronous machine from GRUCAD, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Brazil (the geometry of pmsm is a simplified version of pmsm_cbmag)[1][2][3]
- lomonova.pro: an eight-pole permanent magnet machine [4]
- wfsm_4p.pro: a four-pole wound field synchronous machine [5]
- t30.pro: an simple induction motor with solid rotor [6]
- im_3kw.pro: a four-pole induction machine [7][8][9]
- im.pro: a four-pole deep-bar induction machine [10]
References
<references \>
Models developed by R. Sabariego, J. Gyselinck and C. Geuzaine. This work was funded in part by the Walloon Region (WBGreen No 1217703 FEDO, WIST3 No 1017086 ONELAB) and by the Belgian Science Policy (IAP P7/02). Copyright (c) 2012-2015 ULg-ULB.
|

