Difference between revisions of "Domain decomposition methods for waves"
(→Introduction) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
To run the model, open '''waveguide3d.pro''' with Gmsh. (This is for demonstration uses only. For actual, parallel computations, you should [https://geuz.org/trac/getdp/wiki/ForDavid compile GetDP and Gmsh with MPI support] and [http://onelab.info/files/ddm_wave_simple/run_slurm.sh run the examples from the command line on an HPC cluster].) | To run the model, open '''waveguide3d.pro''' with Gmsh. (This is for demonstration uses only. For actual, parallel computations, you should [https://geuz.org/trac/getdp/wiki/ForDavid compile GetDP and Gmsh with MPI support] and [http://onelab.info/files/ddm_wave_simple/run_slurm.sh run the examples from the command line on an HPC cluster].) | ||
| − | The formulations implement non-overlapping Schwarz domain decomposition methods for the Helmholtz equation and for the time-harmonic Maxwell system. Several families of transmission conditions are implemented: zeroth- and second-order optimized conditions, as well as new Padé-localized square-root conditions<ref name=BoubAntGeuz2012 />. | + | The formulations implement non-overlapping Schwarz domain decomposition methods for the Helmholtz equation and for the time-harmonic Maxwell system. Several families of transmission conditions are implemented: zeroth- and second-order optimized conditions<ref name=Despres1 /><ref name=Despres2 /><ref name=Gander1 /><ref name=Gander2 />, as well as new Padé-localized square-root conditions<ref name=BoubAntGeuz2012 />. |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Despres1>B. Després, Méthodes de Décomposition de Domaine pour les Problèmes de Propagation d'Ondes en Régime Harmonique. Le Théorème de Borg pour l'Equation de Hill Vectorielle, PhD Thesis, Paris VI University, France, 1991.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Despres2>B. Després, P. Joly and J. Roberts, A domain decomposition method for the harmonic Maxwell equations, Iterative methods in linear algebra (Brussels, 1991), pp. 475-484, North-Holland, 1992.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Gander1>M. Gander, F. Magoulès and F. Nataf, Optimized Schwarz methods without overlap for the Helmholtz equation}, | ||
| + | SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 24(1), pp. 38-60, 2002.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Gander2>V. Dolean, M. Gander and L. Gerardo-Giorda, Optimized Schwarz methods for Maxwell's equations, | ||
| + | SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 31(3), pp. 2193-2213, 2009.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Boubendir1>A. Bendali and Y. Boubendir, Non-Overlapping Domain Decomposition Method for a Nodal Finite | ||
| + | Element Method, Numerische Mathematik 103(4), pp.515-537, (2006).</ref> | ||
<ref name=BoubAntGeuz2012>Y. Boubendir, X. Antoine, C. Geuzaine. [http://www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~geuzaine/preprints/ddm_helmholtz_preprint.pdf A quasi-optimal non-overlapping domain decomposition algorithm for the Helmholtz equation]. Journal of Computational Physics 231 (2), 262-280, 2012.</ref> | <ref name=BoubAntGeuz2012>Y. Boubendir, X. Antoine, C. Geuzaine. [http://www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~geuzaine/preprints/ddm_helmholtz_preprint.pdf A quasi-optimal non-overlapping domain decomposition algorithm for the Helmholtz equation]. Journal of Computational Physics 231 (2), 262-280, 2012.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 21 May 2014
|
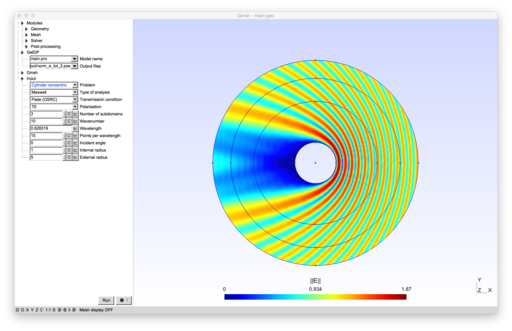
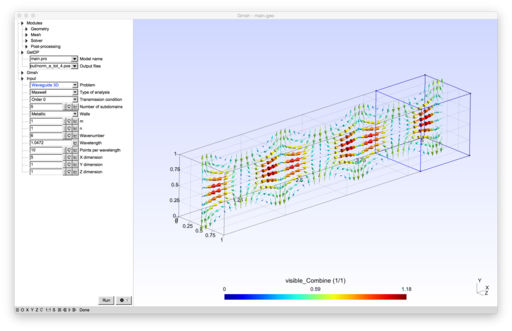
Optimized Schwarz domain decomposition methods for time-harmonic wave problems
|
|
|---|
|
Download model archive (ddm_wave_simple.zip) |
Introduction
To run the model, open waveguide3d.pro with Gmsh. (This is for demonstration uses only. For actual, parallel computations, you should compile GetDP and Gmsh with MPI support and run the examples from the command line on an HPC cluster.)
The formulations implement non-overlapping Schwarz domain decomposition methods for the Helmholtz equation and for the time-harmonic Maxwell system. Several families of transmission conditions are implemented: zeroth- and second-order optimized conditions[1][2][3][4], as well as new Padé-localized square-root conditions[5].
References
- ↑ B. Després, Méthodes de Décomposition de Domaine pour les Problèmes de Propagation d'Ondes en Régime Harmonique. Le Théorème de Borg pour l'Equation de Hill Vectorielle, PhD Thesis, Paris VI University, France, 1991.
- ↑ B. Després, P. Joly and J. Roberts, A domain decomposition method for the harmonic Maxwell equations, Iterative methods in linear algebra (Brussels, 1991), pp. 475-484, North-Holland, 1992.
- ↑ M. Gander, F. Magoulès and F. Nataf, Optimized Schwarz methods without overlap for the Helmholtz equation}, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 24(1), pp. 38-60, 2002.
- ↑ V. Dolean, M. Gander and L. Gerardo-Giorda, Optimized Schwarz methods for Maxwell's equations, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 31(3), pp. 2193-2213, 2009.
- ↑ Y. Boubendir, X. Antoine, C. Geuzaine. A quasi-optimal non-overlapping domain decomposition algorithm for the Helmholtz equation. Journal of Computational Physics 231 (2), 262-280, 2012.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Boubendir1" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
|
Models developed by X. Antoine, Y. Boubendir, M. El Bouajaji, D. Colignon, C. Geuzaine, N. Marsic, B. Thierry, S. Tournier and A. Vion. This work was funded in part by the Belgian Science Policy (IAP P6/21 and P7/02), the Belgian French Community (ARC 09/14-02), the Walloon Region (WIST3 No 1017086 ONELAB and ALIZEES), the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR-09-BLAN-0057-01 MicroWave) and the EADS Foundation (grant 089-1009-1006 High-BRID).
|

