Difference between revisions of "Superconducting wire"
From ONELAB
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
To run the model, open '''helix.pro''' with Gmsh. | To run the model, open '''helix.pro''' with Gmsh. | ||
| − | + | The model uses a 3D H-formulation and the Gmsh cohomology solver <ref name= Pellika2013 /><ref name=Stenvall2014 />. The nonlinear superconductor material law $\rho=\frac{E_c}{J_c}(\frac{\|\vec{J}\|}{J_c})^{n-1}$ is linearized as in <ref name=Kameni2012 />. | |
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| − | <ref name= | + | <ref name=Pellika2013> M. Pellikka, S. Suuriniemi, L. Kettunen and C. Geuzaine, [http://geuz.org/gmsh/doc/preprints/gmsh_homology_preprint.pdf Homology and cohomology computation in finite element modeling]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 35(5), pp. 1195-1214, 2013.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | <ref name=Stenvall2014>A. Stenvall, V. Lahtinen and M. Lyly. An H-formulation-based three-dimensional hysteresis loss modelling tool in a simulation including time varying applied field and transport current: the fundamental problem and its solution. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 27 (2014) 104004 (7pp)</ref> | ||
<ref name=Kameni2012>A. Kameni, J. Lambrechts, J.-F. Remacle, S. Mezani, F. Bouillaut and C. Geuzaine. [http://orbi.ulg.ac.be/handle/2268/113659 Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Computing Induced Fields in Superconducting Materials]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 48(2), pp 591-594, 2012.</ref> | <ref name=Kameni2012>A. Kameni, J. Lambrechts, J.-F. Remacle, S. Mezani, F. Bouillaut and C. Geuzaine. [http://orbi.ulg.ac.be/handle/2268/113659 Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Computing Induced Fields in Superconducting Materials]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 48(2), pp 591-594, 2012.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</references> | </references> | ||
{{metamodelfooter|superconductors}} | {{metamodelfooter|superconductors}} | ||
Revision as of 08:13, 28 July 2015
|
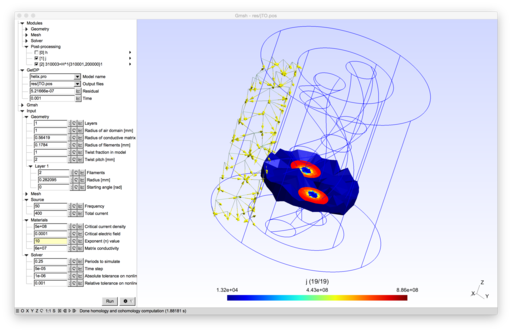
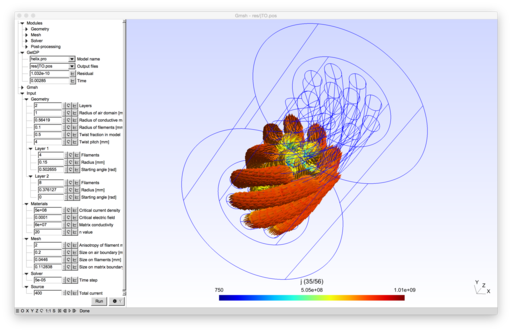
2D and 3D models of superconducting wires.
|
|
|---|
|
Download model archive (superconductors.zip) |
Additional information
To run the model, open helix.pro with Gmsh.
The model uses a 3D H-formulation and the Gmsh cohomology solver [1][2]. The nonlinear superconductor material law $\rho=\frac{E_c}{J_c}(\frac{\|\vec{J}\|}{J_c})^{n-1}$ is linearized as in [3].
References
- ↑ M. Pellikka, S. Suuriniemi, L. Kettunen and C. Geuzaine, Homology and cohomology computation in finite element modeling. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 35(5), pp. 1195-1214, 2013.
- ↑ A. Stenvall, V. Lahtinen and M. Lyly. An H-formulation-based three-dimensional hysteresis loss modelling tool in a simulation including time varying applied field and transport current: the fundamental problem and its solution. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 27 (2014) 104004 (7pp)
- ↑ A. Kameni, J. Lambrechts, J.-F. Remacle, S. Mezani, F. Bouillaut and C. Geuzaine. Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Computing Induced Fields in Superconducting Materials. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 48(2), pp 591-594, 2012.
|
Model developed by C. Geuzaine, A. Kameni and A. Stenvall.
|

