Difference between revisions of "Elmer"
(→CRYO) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
It is developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry. | It is developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry. | ||
| − | = Getting started = | + | = Getting started with the Virtual Machine = |
| − | + | ;Step 1: '''Install Virtual Box''' | |
| − | If you don't have a virtualization utility already installed on your system, | + | :If you don't have a virtualization utility already installed on your system, go to the [https://www.virtualbox.org Oracle VirtualBox website] to download a binary package suitable for your host operating system. Follow the [https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch01.html#intro-installing documentation] to install the software components and to start the VirtualBox Manager. |
| − | go to the [https://www.virtualbox.org Oracle VirtualBox website] | ||
| − | to download a binary package suitable for your host operating system. | ||
| − | Follow the [https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch01.html#intro-installing documentation] | ||
| − | to install the software components and to start the VirtualBox Manager. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
In the VirtualBox Manager, check that a "Host only Network" vboxnet0 is present and properly configured with an active DHCP server | In the VirtualBox Manager, check that a "Host only Network" vboxnet0 is present and properly configured with an active DHCP server | ||
| Line 16: | Line 12: | ||
--> | --> | ||
| − | + | ;Step 2: '''Download the Virtual Machine ONELAB_VM''' | |
| + | :[http://sites.uclouvain.be/immc/mema/alain/ubuntuPLOS-i386-latest.ova Virtual Machine] | ||
| + | :[http://sites.uclouvain.be/immc/mema/alain/ubuntuPLOSi386-latest.ova.sha1 SHA1 checksum] | ||
| − | [ | + | ;Step 3: '''Import the Virtual Machine in Virtual Box''' |
| + | :In the VirtualBox Manager, import the downloaded OVA file by following the [https://www.virtualbox.org/manual/ch01.html#ovf instructions]. A new VM entry - named ONELAB_VM appears in the left panel. | ||
| − | + | ;Step 4: '''Start the Virtual Machine''' | |
| + | :Start the VM by double clicking its entry in the VirtualBox Manager. Enter "plos" for login and "plos" again for password (without quotes) | ||
| − | + | ;Step 5: | |
| − | + | :Open the Firefox browser of the Virtual Machine, reload this page and proceed from within the Virtual Machine. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Open the Firefox browser of the Virtual Machine, reload this page and proceed from within the Virtual Machine. | ||
<!-- Do not delete | <!-- Do not delete | ||
| Line 50: | Line 42: | ||
[[File:CryoEngineering.png|CryoEngineering.png|300px|thumb|right|Cryo-engineering metamodel]] | [[File:CryoEngineering.png|CryoEngineering.png|300px|thumb|right|Cryo-engineering metamodel]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == BEAM == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Download and inflate the archive [http://onelab.info/files/elmerfem/beam.zip beam.zip] in a work directory. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == LASER == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Download and inflate the archive [http://onelab.info/files/elmerfem/laser.zip laser.zip] in a work directory. Then right-click on the icon <code>cryo.ol</code> and opent it with <code>gmsh</code>. Alternatively, start <code>gmsh</code> and click File-> Open-> laser.ol from the menu. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The physical background of this model is the laser stimulation of skin in order to measure the density of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nociceptionreceptors nociceptive] receptors. For a correct interpretation of the experimental data, an accurate nowledge of the temperature distribution in time and across the skin is needed. The metamodel allows selecting various laser types (Gaussian, flat-top) and various stimus characteristics (imposed flux or controlled temperature). Each simulation generates a Gnuplot graphical output that is directly interpretable by clinicians. | ||
| + | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 65: | Line 69: | ||
In order to automize the task, an automatic login from host A to host B is needed so as to avoid entering constantly the password | In order to automize the task, an automatic login from host A to host B is needed so as to avoid entering constantly the password | ||
as explained here: http://linuxproblem.org/art_9.html | as explained here: http://linuxproblem.org/art_9.html | ||
| − | - | + | --> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 14:09, 2 October 2013
Elmer is an open source (GPL) computational tool for multi-physics problems. It is developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry.
Getting started with the Virtual Machine
- Step 1
- Install Virtual Box
- If you don't have a virtualization utility already installed on your system, go to the Oracle VirtualBox website to download a binary package suitable for your host operating system. Follow the documentation to install the software components and to start the VirtualBox Manager.
- Step 2
- Download the Virtual Machine ONELAB_VM
- Virtual Machine
- SHA1 checksum
- Step 3
- Import the Virtual Machine in Virtual Box
- In the VirtualBox Manager, import the downloaded OVA file by following the instructions. A new VM entry - named ONELAB_VM appears in the left panel.
- Step 4
- Start the Virtual Machine
- Start the VM by double clicking its entry in the VirtualBox Manager. Enter "plos" for login and "plos" again for password (without quotes)
- Step 5
- Open the Firefox browser of the Virtual Machine, reload this page and proceed from within the Virtual Machine.
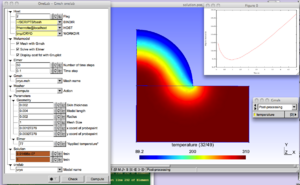
CRYO
Download and inflate the archive cryo.zip in a work directory.
Then right-click on the icon cryo.ol and opent it with gmsh. Alternatively, start gmsh and click File-> Open-> cryo.ol from the menu.
The physical background is the cryogenic treatment of warts by application of a cryogenic fluid. The idea is to maximize the destruction of wart tissue cells while minimizing damages to healthy skin tissue. A damage function depending on temperature distribution and exposure time is built to represent this trade-off. The purpose of the modeling is to determine the application time that minimizes this damage function.
Various geometrical and modeling parameters can be interactively modified in the ONELAB window.
After execution, a plot of the damage function vs. time is displayed and the optimum application time tmin is shown to the ONELAB window.
BEAM
Download and inflate the archive beam.zip in a work directory.
LASER
Download and inflate the archive laser.zip in a work directory. Then right-click on the icon cryo.ol and opent it with gmsh. Alternatively, start gmsh and click File-> Open-> laser.ol from the menu.
The physical background of this model is the laser stimulation of skin in order to measure the density of nociceptive receptors. For a correct interpretation of the experimental data, an accurate nowledge of the temperature distribution in time and across the skin is needed. The metamodel allows selecting various laser types (Gaussian, flat-top) and various stimus characteristics (imposed flux or controlled temperature). Each simulation generates a Gnuplot graphical output that is directly interpretable by clinicians.