Elmer
Elmer is an open source (GPL) computational tool for multi-physics problems. It is developed by CSC in collaboration with Finnish universities, research laboratories and industry.
Two complete metamodels using Elmer are available on the read-only svn distribution of gmsh, which can be downloaded from geuz.org/gmsh.
You also need a working recent (nightly-build) version of gmsh to be executable on your system.
First take a look at this tutorial to see how ONELAB can be installed.
LASER
The cryo-engineering metamodel "LASER" is launched as follows:
- export GMSH_DIR=/path/to/your/gmsh/directory
- cd $GMSH_DIR/projects/onelab/METAMODELS/CRYO
- gmsh circle.geo -s
The "-s" option amounts to click on "Tool/Onelab" in the Gmsh menu.
The physical background of this model is the laser stimulation of skin in order to measure the density of [[1]] receptors. For a correct interpretation of the experimental data, an accurate nowledge of the temperature distribution in time and across the skin is needed. The metamodel allows selecting various models of stimulation (imposed flux, imposed temperature and controlled temperature) and various laser types (Gaussian or flat-top). Each simulation generates a Matlab or Gnuplot graphical output that is directly interpretable by clinicians. Check in the "lab_peau.ol" file how the switch between Matlab and Gnuplot is done, and modify the file if necessary according to your system settings.
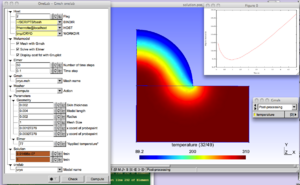
CRYO
The cryo-engineering metamodel "CRYO" is launched as follows:
- export GMSH_DIR=/path/to/your/gmsh/directory
- cd $GMSH_DIR/projects/onelab/METAMODELS/CRYO
- gmsh circle.geo -s
The physical background is the cryogenic treatment of warts by application of a cryogenic fluid. The idea is to maximize the destruction of wart tissue cells while minimizing damages done to healthy skin tissue. An damage function depending on temperature distribution and time is built to represent this trade-off and the purpose of the modeling is to determine the application time that minimizes this damage function.
Various geometrical and modeling parameters can be interactively modified in the ONELAB window.
After execution, a plot of the damage function displayed and the optimum application time tmoin is uploaded to the ONELAB window.