ONELAB
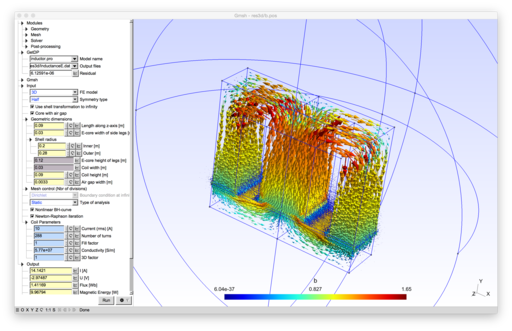
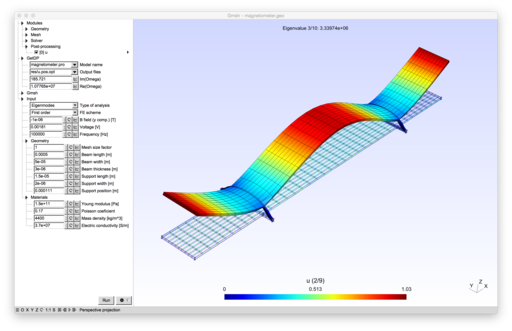
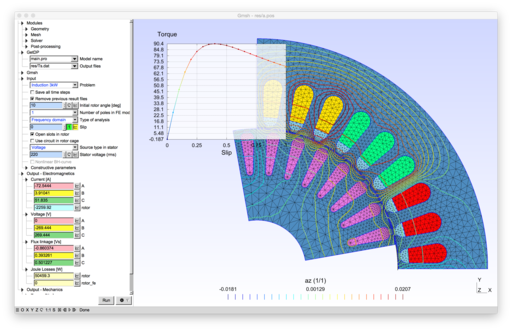
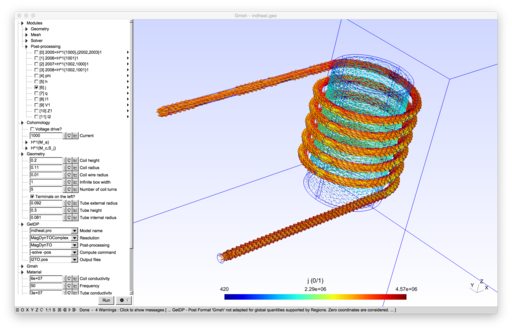
ONELAB (Open Numerical Engineering LABoratory) is a free, lightweight interface to finite element software for engineering applications. It allows calling sequences of independent clients (e.g. mesh generators, finite element solvers and other related tools) and have them share parameters and modeling information. ONELAB is fully open source.
Give it a try!
- Download ONELAB:
- Desktop version for Windows, Linux and MacOSX (no installation necessary: simply uncompress the ZIP file)
- Mobile version for Android and iOS
- Launch ONELAB (for the desktop version, double-click on the Gmsh executable, e.g. gmsh.exe Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destinationon Windows)
- Open a model:
- Desktop version: load one of the GetDP models (.pro file) through the File/Open menu, e.g. inductor.pro in the models/inductor directory.
- Mobile version: simply select one of the preloaded models
- Press Run.
- ... then explore other models!
Use existing clients
Native clients directly embed the ONELAB library:
- GetDP: a finite element solver for electromagnetism, heat transfer, acoustics and generic PDEs
- Gmsh: a mesh generator and post-processor (Gmsh also plays the role of ONELAB server)
- Onelab/Mobile: GetDP and Gmsh on iPhone, iPad and Android devices
Other clients (non-native) are interfaced with ONELAB by a system of input file pre-processing. The different steps of a simulation (meshing, solving, post-processing) are controlled by a python script. See worked-out examples with:
- Elmer: a finite element solver for multi-physic problems developed by CSC
- OpenFOAM: an open source CFD software package developed by OpenCFD
Any software driven by input data files (e.g. Code_Aster, Abaqus, CalculiX, FreeFem, Gnuplot, ...) can be readily interfaced in the same way.
Here are some useful hints to efficiently use the ONELAB graphical user interface.
Develop your own client
Implement your own native ONELAB clients:
- With Python: any Python code can become a native ONELAB client
- With C++: how to create a native C++ ONELAB client
Technical information
The ONELAB interface is based on an abstraction of the interface to finite element solvers and related tools: for geometry modeling and meshing, for the definition of physical properties, constraints and other solver parameters, and for post-processing.
The implementation is based on a client-server model, with a server-side database and (optional) graphical front-end, and local or remote clients communicating in-memory or through TCP/IP sockets. Contrary to most available solver interfaces, the ONELAB server has no a priori knowledge about any specifics (input file format, syntax, ...) of the clients. In practice, this is made possible by having any simulation preceded by an analysis phase, during which the clients are asked to upload their parameter set to the server.
Native ONELAB clients can be written in C++ or Python, and embed the ONELAB library. For native clients the specification of which data to share is completely dynamic. For non-native clients, the ONELAB server acts as a pre-processor of their input files, which should be instrumented to specify the information to be shared. In all cases the issues of completeness and consistency of the parameter sets are completely dealt with on the client side: the role of ONELAB is limited to data centralization, modification and re-dispatching.
The ONELAB project was funded by the Walloon Region under WIST3 grant n° 1017086.



